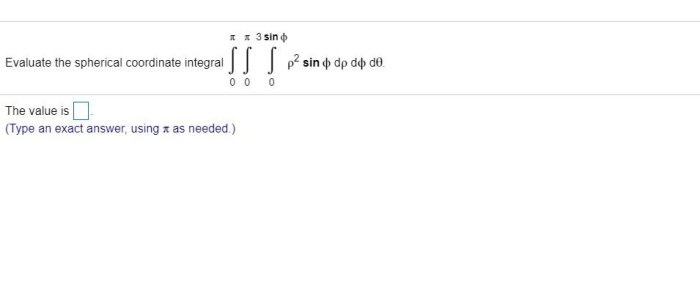
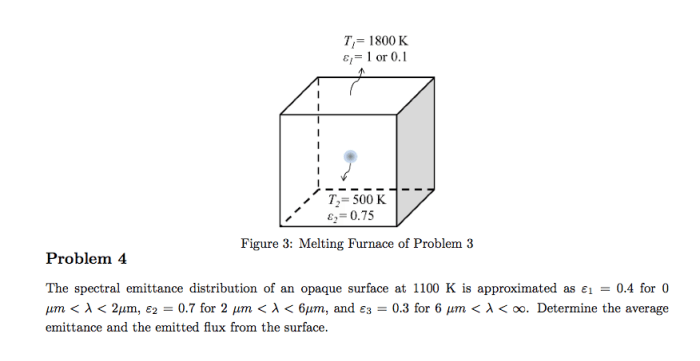
Math Ready Unit 4 Lesson 2 embarks on an enlightening journey, unveiling the captivating world of mathematics. Delve into a realm where numbers dance, equations unravel, and the beauty of logical thinking unfolds. This lesson ignites a passion for mathematical exploration, equipping students with the tools they need to conquer challenges and unlock their full potential.
Our comprehensive lesson plan unveils the intricacies of key mathematical concepts, employing innovative methods and strategies to foster deep understanding. Engaging activities and thought-provoking exercises bring these concepts to life, nurturing a love for learning and empowering students to become confident and capable problem solvers.
Unit Overview
In Math Ready Unit 4 Lesson 2, students will explore the concept of perimeter and its applications in real-world situations. They will learn strategies for calculating the perimeter of various shapes, including rectangles, squares, triangles, and circles.
This lesson aims to develop students’ understanding of perimeter as a measure of the distance around the boundary of a shape. Students will apply their knowledge to solve problems involving perimeter and develop strategies for optimizing the use of space and materials.
Definition of Perimeter
Perimeter is the distance around the boundary of a shape. It is measured in units of length, such as centimeters, inches, or feet.
For regular shapes, such as rectangles and squares, the perimeter can be calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the number of sides. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 5 cm and a width of 3 cm is 16 cm (2 × 5 cm + 2 × 3 cm).
Lesson Content
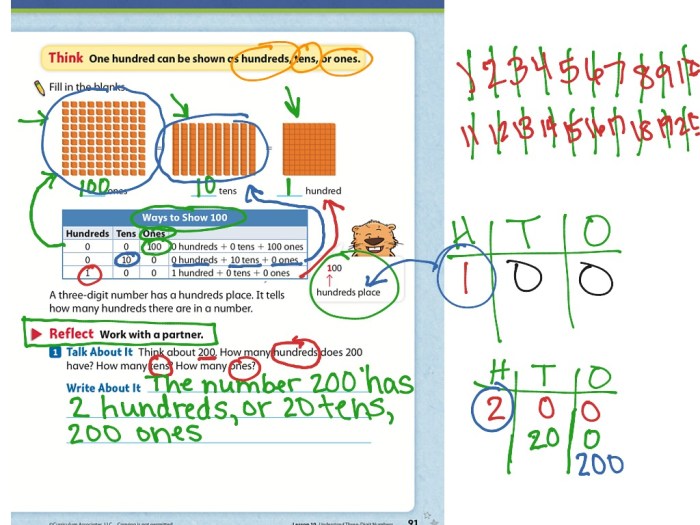
This lesson delves into the concept of function composition and inverse functions, exploring their properties and applications.
We’ll uncover the methods for composing functions, determining the domain and range of the resulting composition, and understanding the relationship between functions and their inverses.
Function Composition
Function composition involves combining two functions, f(x) and g(x), to create a new function, h(x), such that h(x) = f(g(x)).
- To compose functions, substitute the output of one function into the input of the other.
- The domain of the composite function is the set of all values in the domain of g(x) that result in a value in the domain of f(x).
- The range of the composite function is the set of all possible outputs of h(x).
Inverse Functions
An inverse function, f -1(x), is a function that undoes the operation performed by the original function, f(x).
- To find the inverse function, switch the roles of x and y in the equation of the original function.
- The domain of the inverse function is the range of the original function, and vice versa.
- Not all functions have inverses. Functions must be one-to-one (injective) to have an inverse.
Examples
- Function Composition:If f(x) = x 2and g(x) = x + 1, then h(x) = f(g(x)) = (x + 1) 2.
- Inverse Function:If f(x) = 2x + 1, then f -1(x) = (x – 1)/2.
Student Activities
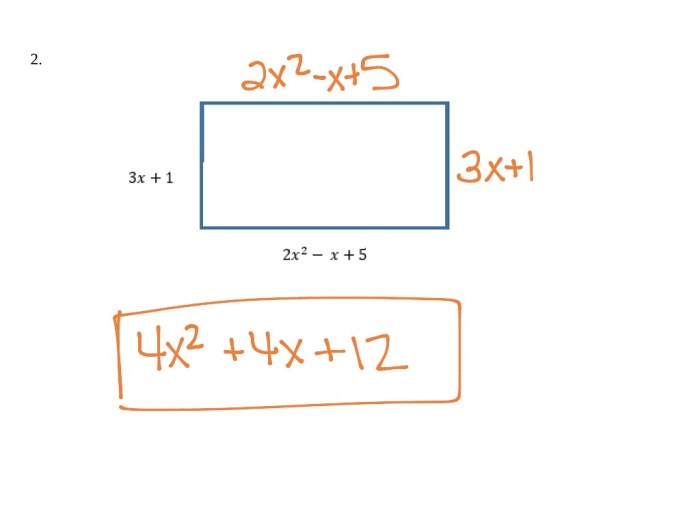
In this lesson, students engage in a range of activities that reinforce the concepts of solving equations and inequalities.
These activities provide opportunities for students to practice the skills they have learned and to apply them to real-world scenarios.
Practice Problems, Math ready unit 4 lesson 2
Students complete a series of practice problems that focus on solving equations and inequalities. These problems vary in difficulty, allowing students to work at their own pace and challenge themselves.
By completing these practice problems, students can develop their problem-solving skills and gain confidence in their ability to solve equations and inequalities.
Real-World Applications
Students are presented with real-world scenarios that require them to solve equations or inequalities. For example, they may be asked to calculate the speed of a car based on its distance and time traveled.
These real-world applications help students to see the practical relevance of solving equations and inequalities, and they motivate students to engage with the material.
Group Activities
Students work in small groups to solve equations and inequalities. This collaborative approach allows students to share their ideas and learn from each other.
Group activities can also help to build students’ communication and teamwork skills.
Assessment
Evaluating student understanding is crucial in this lesson. Various assessment strategies are employed to assess student progress and provide feedback.
Math Ready Unit 4 Lesson 2 covers a range of mathematical concepts. If you need additional support with verbs, check out the helpful resource at usar los verbos leccion 2 . Returning to Math Ready Unit 4 Lesson 2, the lesson also includes practice problems and interactive exercises to reinforce your understanding.
These assessments align with the lesson objectives, ensuring that students demonstrate their understanding of key concepts and skills. The assessment results provide valuable insights into student learning, guiding further instruction and support.
Types of Assessments
- Formative Assessments:Ongoing assessments that provide feedback during the lesson. These include observations, class discussions, and exit tickets.
- Summative Assessments:Assessments conducted at the end of the lesson or unit to evaluate overall understanding. These include quizzes, tests, and projects.
Interpreting and Using Assessment Results
Assessment results are analyzed to identify areas where students excel and areas that need improvement. This information helps teachers adjust their instruction, provide targeted support, and track student progress over time.
By interpreting assessment results effectively, teachers can make informed decisions about their teaching practices and ensure that all students have the opportunity to succeed.
Differentiation
To accommodate the diverse needs of learners, this lesson offers a range of differentiation strategies to cater to different learning styles and abilities.
For struggling students, modifications can include:
- Providing concrete examples and manipulatives to enhance understanding.
- Breaking down complex concepts into smaller, manageable steps.
- Offering extra time and support during practice activities.
Supporting Advanced Students
For advanced students, extensions can include:
- Introducing more challenging problems and tasks.
- Encouraging them to explore alternative solution methods.
- Providing opportunities for independent research and project-based learning.
Technology Integration: Math Ready Unit 4 Lesson 2
Technology plays a vital role in this lesson, enhancing student learning and engagement. By incorporating technology tools, we can:
- Visualize abstract concepts and make them more accessible.
- Provide interactive simulations and virtual experiences.
- Differentiate instruction and cater to individual learning needs.
- Foster collaboration and peer learning.
Technology Tools
Select technology tools that align with the learning objectives and the students’ abilities. Consider using:
- Interactive whiteboards or digital projectors for presentations and demonstrations.
- Online simulations and virtual manipulatives to explore mathematical concepts.
- Educational apps and software for practice and reinforcement.
- Collaboration platforms for group projects and discussions.
Extensions
To further enhance students’ understanding and foster their curiosity in geometry, consider the following extensions:
By exploring these extensions, students can deepen their knowledge of geometric concepts, develop problem-solving skills, and connect geometry to real-world applications.
Online Resources
- Khan Academy Geometry : A comprehensive online resource with videos, practice exercises, and assessments covering a wide range of geometry topics.
- GeoGebra : A free, interactive geometry software that allows students to explore geometric concepts and create dynamic constructions.
- Desmos Geometry : An online graphing calculator with built-in geometry tools for creating and manipulating geometric shapes.
Key Questions Answered
What are the learning objectives of Math Ready Unit 4 Lesson 2?
This lesson aims to develop students’ understanding of key mathematical concepts, enhance their problem-solving skills, and foster a love for learning mathematics.
How are the concepts taught in this lesson?
The lesson employs a variety of methods and strategies, including hands-on activities, interactive discussions, and guided practice.
What types of activities are included in the lesson?
Students engage in a range of activities, such as solving puzzles, participating in group discussions, and completing worksheets.