Isotopes and atomic mass answer key – Embark on a journey to unravel the intricate world of isotopes and atomic mass, where the fundamental building blocks of matter reveal their secrets. This answer key unveils the concepts, applications, and interrelationships that shape our understanding of these essential elements in chemistry.
From defining isotopes and deciphering their notation to exploring the intricacies of atomic mass calculation and its impact on element composition, this guide provides a comprehensive roadmap through the fascinating realm of isotopes and atomic mass.
Isotopes
Isotopes are variations of the same chemical element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. The number of protons determines the element, while the number of neutrons determines the isotope. Isotopes have the same chemical properties but different physical properties, such as mass and radioactivity.
Notation of Isotopes
Isotopes are represented by the chemical symbol of the element followed by a superscript indicating the mass number, which is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. For example, carbon-12 ( 12C) has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, while carbon-14 ( 14C) has 6 protons and 8 neutrons.
Applications of Isotopes
Isotopes have a wide range of applications in science, medicine, and industry.
- Radioactive isotopes are used in medicine for diagnosis and treatment of diseases, such as cancer.
- Stable isotopes are used in geochemistry to study the age of rocks and fossils.
- Isotopes are used in industry to trace the flow of materials and to study the properties of materials.
Atomic Mass
Atomic mass is the weighted average mass of all the isotopes of an element. It is expressed in atomic mass units (amu), which are defined as 1/12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
To calculate the atomic mass of an element, we need to know the mass and abundance of each of its isotopes. The weighted average atomic mass is then calculated as follows:
- Multiply the mass of each isotope by its abundance.
- Add up the products from step 1.
- Divide the sum from step 2 by the total abundance of all the isotopes.
Weighted Average Atomic Mass
The weighted average atomic mass is a useful concept because it allows us to determine the average mass of the atoms of an element in a sample. This information can be used to calculate the molar mass of a compound, which is the mass of one mole of the compound.
For example, the atomic mass of chlorine is 35.45 amu. This means that the average mass of a chlorine atom is 35.45 amu. The molar mass of chlorine is 35.45 g/mol, which means that one mole of chlorine weighs 35.45 grams.
Table of Atomic Masses
The following table lists the atomic masses of some common elements:
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Mass (amu) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H | 1.008 |
| Helium | He | 4.0026 |
| Carbon | C | 12.011 |
| Nitrogen | N | 14.007 |
| Oxygen | O | 15.999 |
| Sodium | Na | 22.990 |
| Magnesium | Mg | 24.305 |
| Aluminum | Al | 26.982 |
| Silicon | Si | 28.085 |
| Chlorine | Cl | 35.45 |
Relationship between Isotopes and Atomic Mass
The presence of isotopes has a significant impact on the atomic mass of an element. Atomic mass is the weighted average mass of all the isotopes of an element, taking into account their relative abundances.
Isotopic Abundance and Atomic Mass, Isotopes and atomic mass answer key
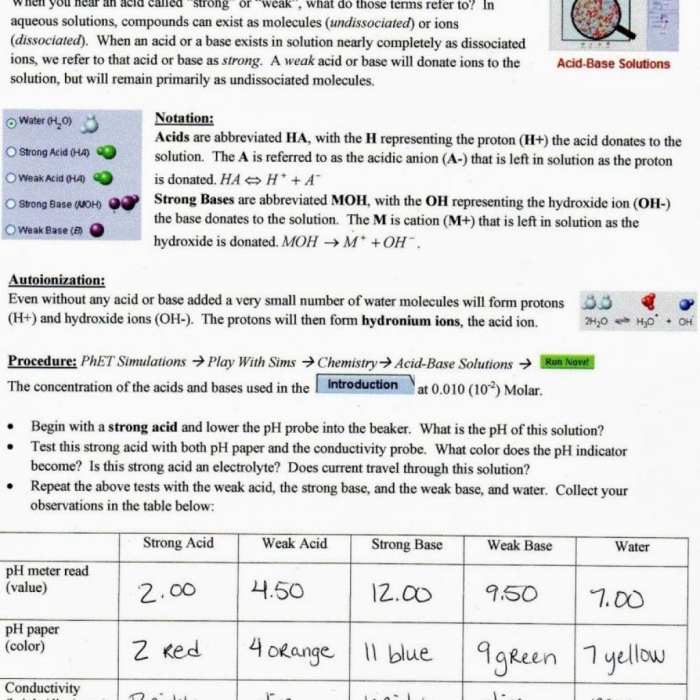
The isotopic abundance of an element refers to the relative proportions of its different isotopes in a naturally occurring sample. Isotopes with higher abundances contribute more to the overall atomic mass. For example, chlorine has two stable isotopes: chlorine-35 (75.77% abundance) and chlorine-37 (24.23% abundance).
The atomic mass of chlorine is calculated as:
Atomic mass of chlorine = (0.7577
- 35 amu) + (0.2423
- 37 amu) = 35.45 amu
Applications of Isotopes and Atomic Mass
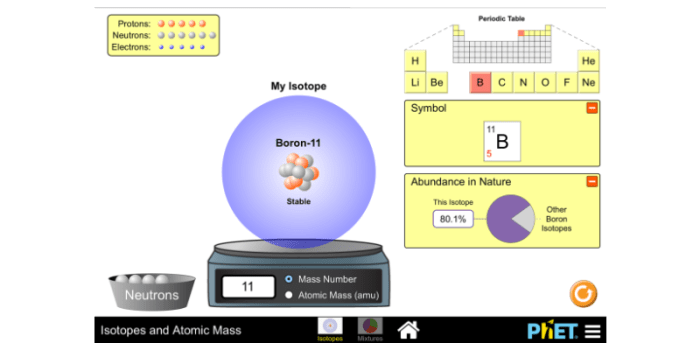
Isotopes and atomic mass find widespread applications in various scientific fields and industries.
Medicine
- Radioisotopes are used in medical imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and PET scans.
- Radioisotopes are used in radiation therapy to treat certain types of cancer.
- Stable isotopes are used in metabolic studies and drug development.
Archaeology
- Radioactive isotopes are used in radiocarbon dating to determine the age of ancient artifacts and fossils.
- Isotopic analysis can provide information about the origin and movement of ancient populations.
Environmental Science
- Isotopes are used to study environmental processes such as water movement, pollution dispersion, and climate change.
- Stable isotopes can be used to trace the sources of pollutants and identify environmental contamination.
Nuclear Chemistry
- Atomic mass is used to calculate the energy released in nuclear reactions.
- Isotopes are used as tracers in nuclear chemistry experiments.
- Isotopes are used in nuclear power plants to generate electricity.
FAQ Explained: Isotopes And Atomic Mass Answer Key
What is the difference between isotopes and atomic mass?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, while atomic mass is the weighted average mass of all isotopes of an element.
How is atomic mass calculated?
Atomic mass is calculated by multiplying the mass of each isotope by its abundance and summing the products.
What are some applications of isotopes?
Isotopes are used in medicine for imaging and treatment, in archaeology for dating artifacts, and in environmental science for tracing pollutants.