In the realm of geometry, the concept of triangle inequalities holds paramount importance in understanding the relationships between the sides and angles of triangles. Unit 5 relationships in triangles homework 8 triangle inequalities delve into the intricacies of these inequalities, providing a comprehensive guide to their applications and significance.
Triangle inequalities serve as fundamental principles that govern the properties and behavior of triangles. They establish relationships between the lengths of sides and the measures of angles, enabling us to solve a wide range of problems involving triangles.
Triangle Inequality Theorem: Unit 5 Relationships In Triangles Homework 8 Triangle Inequalities
The Triangle Inequality Theorem states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side.
This theorem has many applications in geometry, such as:
- Determining whether a triangle is valid
- Finding the shortest path between two points
- Solving problems involving the area and perimeter of triangles
Properties of Triangles
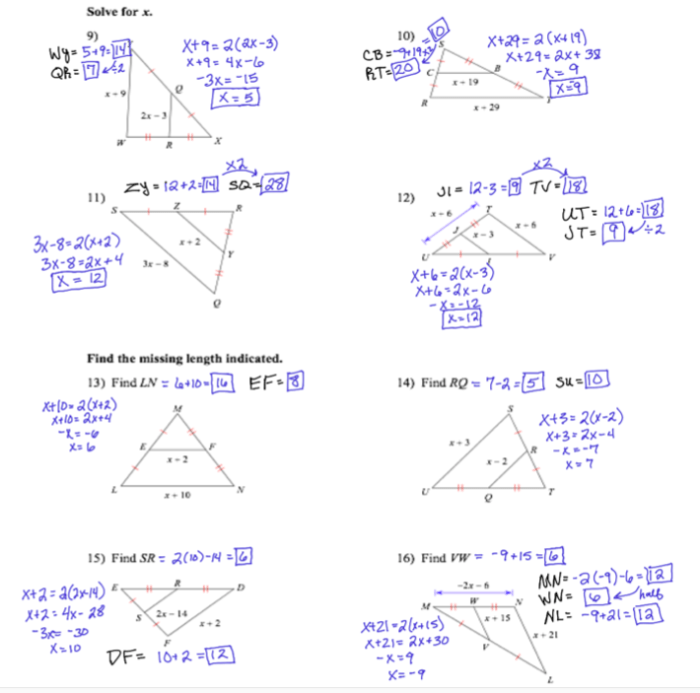
Triangles have many properties that can be used to classify them.
Some of the most important properties of triangles include:
- The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees.
- The longest side of a triangle is opposite the largest angle.
- The median of a triangle is a line segment that connects a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
Triangle Inequalities
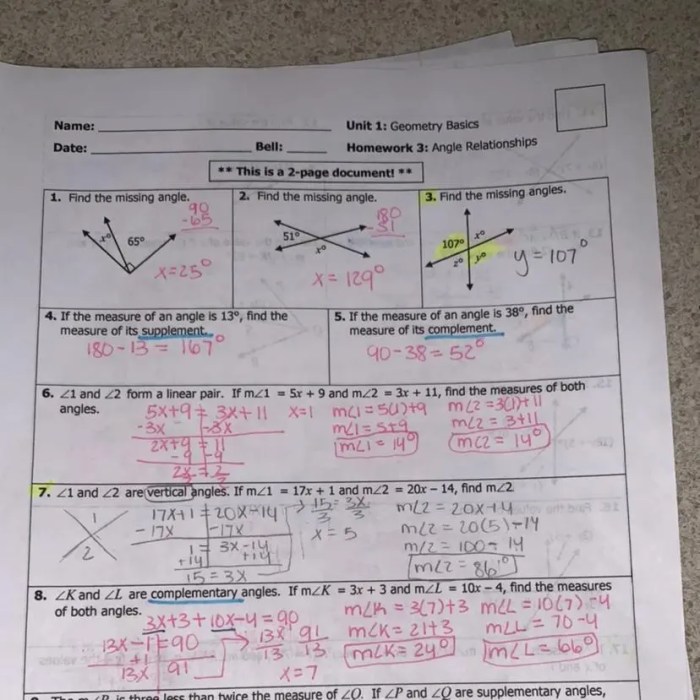
There are two main types of triangle inequalities:
- The triangle inequality states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side.
- The reverse triangle inequality states that the difference between the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be less than the length of the third side.
Applications of Triangle Inequalities
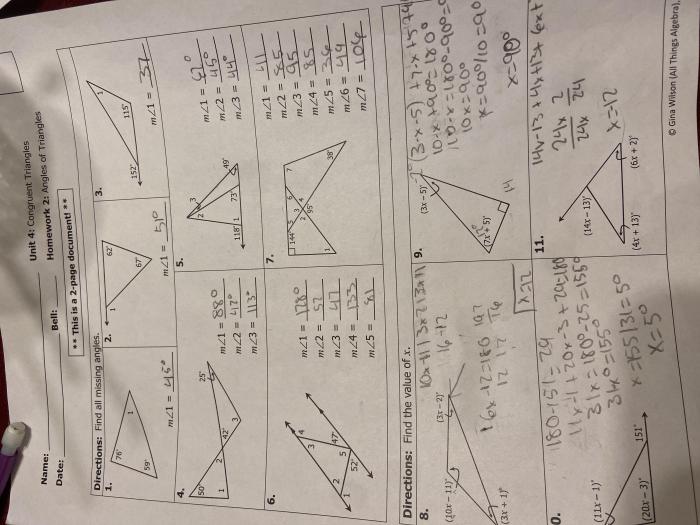
Triangle inequalities have many applications in real-world situations.
Some of the most common applications include:
- Navigation: Triangle inequalities can be used to determine the shortest path between two points.
- Engineering: Triangle inequalities can be used to design structures that are strong and stable.
- Computer science: Triangle inequalities can be used to solve problems in computational geometry.
Examples of Triangle Inequalities
Here are some examples of triangle inequalities:
- In a triangle with sides of length 3, 4, and 5, the triangle inequality states that 3 + 4 > 5.
- In a triangle with sides of length 6, 8, and 10, the reverse triangle inequality states that 10 – 6< 8.
Popular Questions
What is the Triangle Inequality Theorem?
The Triangle Inequality Theorem states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side.
How can triangle inequalities be used to classify triangles?
Triangle inequalities can be used to classify triangles based on the relationships between their side lengths. For example, a triangle with two sides of equal length is classified as an isosceles triangle, while a triangle with three sides of equal length is classified as an equilateral triangle.
What are the applications of triangle inequalities in real-world situations?
Triangle inequalities have numerous applications in real-world situations, such as navigation, engineering, and architecture. For example, in navigation, triangle inequalities can be used to determine the shortest distance between two points.