The intraoral technique of exposing periapical and bitewing images plays a crucial role in dental diagnostics and treatment planning. This comprehensive guide delves into the principles, techniques, equipment, advantages, and limitations of these imaging methods, providing a thorough understanding of their applications in clinical dentistry.
Intraoral periapical imaging captures detailed images of specific teeth and their surrounding structures, while bitewing imaging provides panoramic views of the teeth and jaws. Both techniques utilize specialized equipment and materials to produce high-quality images for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Intraoral Technique for Exposing Periapical Images
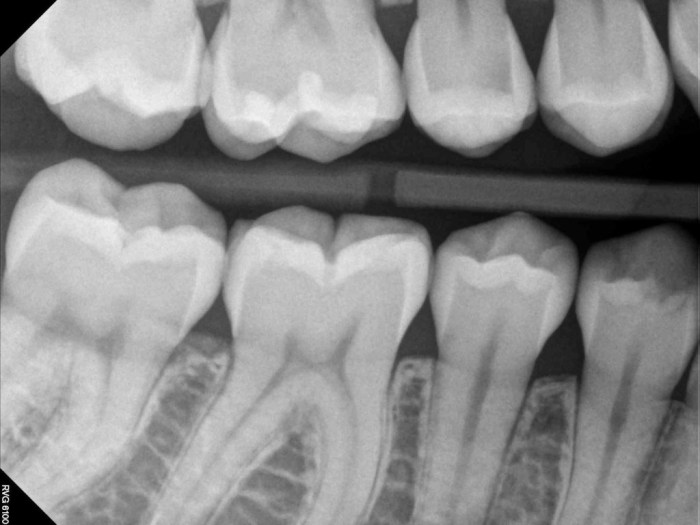
Intraoral periapical imaging involves capturing radiographic images of specific teeth and their surrounding structures using an intraoral X-ray machine.
Principles and Techniques, Intraoral technique of exposing periapical and bitewing images
The technique involves placing an X-ray sensor or film inside the patient’s mouth, positioned against the tooth of interest. The X-ray beam is directed through the tooth and surrounding tissues, capturing an image of the root tip and surrounding bone.
Equipment and Materials
The equipment used in intraoral periapical imaging includes:
- Intraoral X-ray machine
- X-ray sensor or film
- Positioner or bitewing holder
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- Detailed visualization of specific teeth and surrounding structures
- Assessment of root anatomy, caries, and periapical pathology
Limitations:
- Limited field of view, may not capture all areas of interest
- Exposure to ionizing radiation
Intraoral Technique for Exposing Bitewing Images
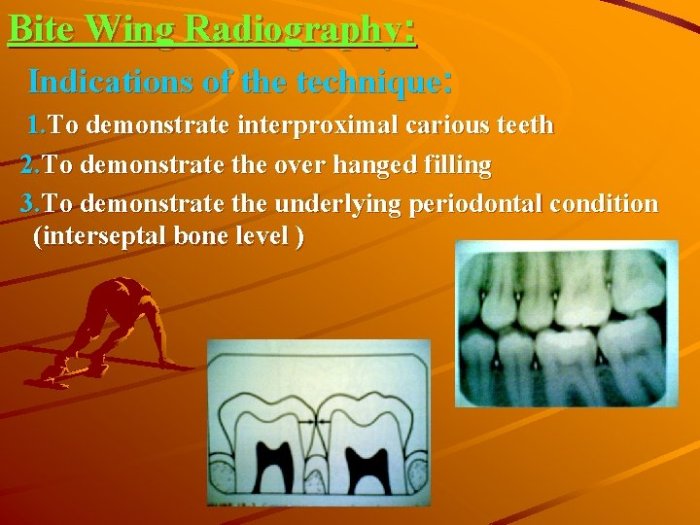
Intraoral bitewing imaging is a technique used to capture radiographic images of the upper and lower teeth in a single exposure.
Principles and Techniques, Intraoral technique of exposing periapical and bitewing images
The technique involves placing a bitewing tab between the patient’s teeth, which aligns the upper and lower teeth for simultaneous exposure. The X-ray beam is directed through the teeth and surrounding tissues, capturing an image of both dental arches.
Equipment and Materials
The equipment used in intraoral bitewing imaging includes:
- Intraoral X-ray machine
- Bitewing tab
- X-ray sensor or film
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- Simultaneous visualization of upper and lower teeth
- Assessment of interproximal caries, periodontal disease, and occlusal relationships
Limitations:
- Limited visualization of root anatomy
- Potential for distortion due to patient movement
Comparison of Intraoral Periapical and Bitewing Techniques
Similarities
- Both techniques use intraoral X-ray machines
- Both involve placing a sensor or film inside the patient’s mouth
Differences
- Field of View:Periapical images focus on a specific tooth, while bitewing images capture both dental arches
- Diagnostic Focus:Periapical images provide detailed information about root anatomy and periapical pathology, while bitewing images focus on interproximal caries and periodontal disease
- Positioning:Periapical images require precise positioning of the sensor against the tooth, while bitewing images utilize a bitewing tab to align the teeth
Appropriate Applications
- Periapical Images:Assessing root anatomy, caries, and periapical pathology
- Bitewing Images:Detecting interproximal caries, periodontal disease, and occlusal relationships
Radiation Safety in Intraoral Imaging: Intraoral Technique Of Exposing Periapical And Bitewing Images
Radiation safety measures are essential in intraoral imaging to minimize exposure to ionizing radiation.
Potential Risks and Benefits
Risks:
- Exposure to ionizing radiation
- Potential for long-term health effects
Benefits:
- Early detection and diagnosis of dental conditions
- Improved patient outcomes
Guidelines for Minimizing Radiation Exposure
- Use appropriate shielding and protective gear
- Optimize exposure parameters (kVp, mAs)
- Collimate the X-ray beam
- Limit the number of exposures
Patient Positioning and Preparation for Intraoral Imaging
Patient Positioning
- Periapical Images:Patient’s head is tilted back slightly, with the sensor or film placed against the tooth of interest
- Bitewing Images:Patient’s head is upright, with the bitewing tab positioned between the upper and lower teeth
Patient Preparation
- Remove any metal objects from the mouth
- Inform the patient about the procedure and potential risks
- Ensure patient comfort and cooperation
Special Considerations
- Children:Use smaller sensors or films, minimize exposure time
- Pregnant patients:Lead apron shielding, minimize exposure
Image Interpretation and Diagnosis
Basic Principles
- Identify normal anatomical structures
- Detect any abnormalities or pathologies
- Correlate findings with patient history and clinical examination
Common Findings
- Caries: Radiolucent areas within the tooth
- Periapical pathology: Radiolucent areas at the root tip
- Periodontal disease: Radiolucent areas along the tooth root
Role in Diagnosis
- Confirming or excluding dental conditions
- Assessing the extent of disease
- Monitoring treatment progress
FAQ Resource
What are the advantages of intraoral periapical imaging?
Intraoral periapical imaging offers high resolution and detailed visualization of specific teeth and their surrounding structures, aiding in the diagnosis of caries, periodontal disease, and periapical lesions.
What is the difference between periapical and bitewing imaging?
Periapical imaging captures images of individual teeth and their roots, while bitewing imaging provides a broader view of the teeth and jaws, including the interproximal surfaces.
What are the radiation safety considerations for intraoral imaging?
Dental professionals must adhere to strict radiation safety protocols to minimize patient exposure. This includes using appropriate shielding, limiting the number of exposures, and employing digital imaging techniques whenever possible.