Bioflix activity how synapses work events at a synapse – Embark on a scientific voyage with our exploration of “Bioflix Activity: How Synapses Work: Events at a Synapse.” This comprehensive guide unravels the intricate mechanisms of synaptic communication, providing a foundation for understanding the brain’s remarkable capabilities.
Delving into the structure and function of synapses, we witness the dynamic interplay of neurotransmitters, receptors, and postsynaptic responses. The role of calcium ions in synaptic transmission emerges as a crucial factor, shaping the efficiency and direction of neural communication.
Bioflix Activity: How Synapses Work
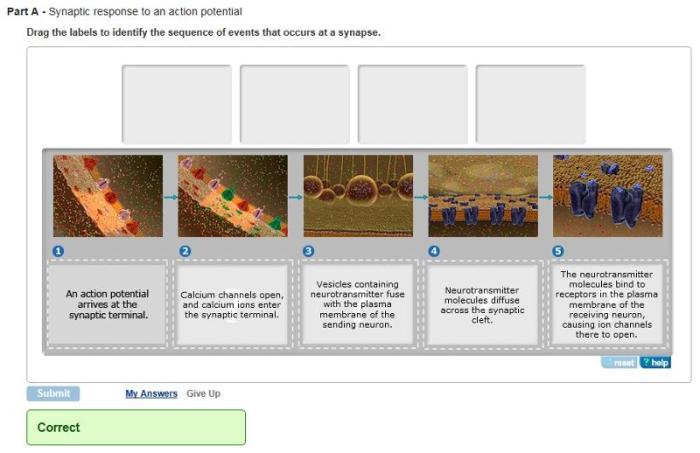
Synapses are the junctions between neurons that allow them to communicate with each other. They are composed of a presynaptic neuron, which releases neurotransmitters, and a postsynaptic neuron, which receives the neurotransmitters. The space between the two neurons is called the synaptic cleft.When
an action potential reaches the presynaptic neuron, it causes the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, which causes a change in the electrical potential of the postsynaptic neuron. This change in electrical potential can either excite or inhibit the postsynaptic neuron, depending on the type of neurotransmitter that is released.Calcium
ions play an important role in synaptic transmission. When an action potential reaches the presynaptic neuron, it causes an influx of calcium ions into the neuron. This influx of calcium ions triggers the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron.
Types of Synapses

There are two main types of synapses: chemical synapses and electrical synapses. Chemical synapses use neurotransmitters to communicate between neurons, while electrical synapses use electrical signals to communicate between neurons.Chemical synapses are the most common type of synapse. They are found in all parts of the nervous system.
Electrical synapses are less common than chemical synapses. They are found in a few specific areas of the nervous system, such as the retina and the spinal cord.
Synaptic Plasticity: Bioflix Activity How Synapses Work Events At A Synapse
Synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to change their strength over time. This change in strength can be either long-term or short-term. Long-term potentiation (LTP) is a long-lasting increase in synaptic strength that is thought to be the basis of learning and memory.
Long-term depression (LTD) is a long-lasting decrease in synaptic strength that is thought to be involved in forgetting.
Synaptic Disorders

Synaptic disorders are a group of disorders that are caused by problems with synapses. These disorders can affect a person’s ability to learn, remember, and think. Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease are two examples of synaptic disorders.Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that is characterized by a progressive loss of memory and cognitive function.
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that is characterized by tremors, rigidity, and slowness of movement.
FAQ Resource
What is the role of calcium ions in synaptic transmission?
Calcium ions act as messengers, triggering neurotransmitter release and influencing synaptic strength.
How does synaptic plasticity contribute to learning and memory?
Synaptic plasticity allows synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, providing a cellular basis for memory formation and learning.