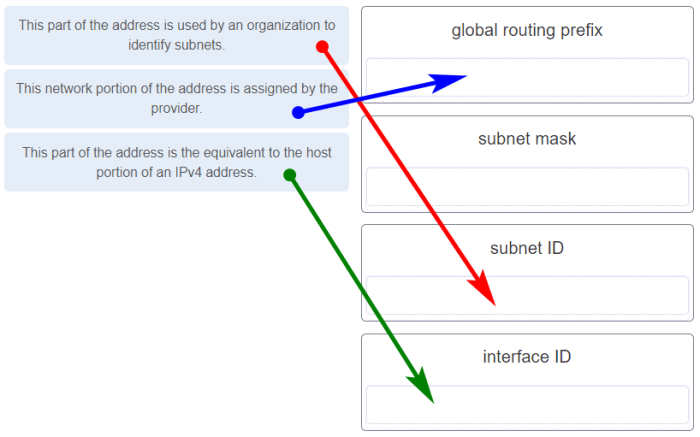
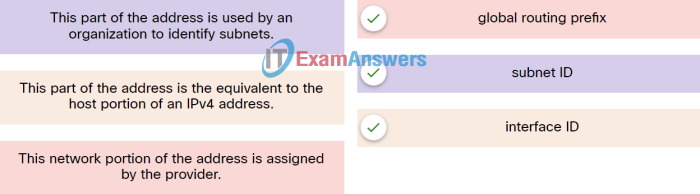
Match the description to the ipv6 addressing component – Delve into the realm of IPv6 addressing components, where each plays a pivotal role in shaping the intricate network infrastructure that connects devices worldwide. From Global Unicast Addresses to Unspecified Addresses, this exploration unveils the purpose, structure, and significance of these fundamental elements.
IPv6 Addressing Components
IPv6 addressing is a hierarchical addressing system used to identify devices on a network. It provides a much larger address space than IPv4, which is necessary for the growing number of devices connected to the Internet. IPv6 addresses are 128 bits long, compared to 32 bits for IPv4 addresses.
This allows for a much larger number of unique addresses.IPv6 addresses are divided into several components, each of which has a specific purpose. The following are the most common IPv6 address components:
Global Unicast Address
A global unicast address is used to identify a single device on the Internet. It is the most common type of IPv6 address. Global unicast addresses are assigned by Internet service providers (ISPs) to devices that connect to the Internet.An
example of a global unicast address is 2001:0db8:85a3:08d3:1319:8a2e:0370:7334.The structure of a global unicast address is as follows:
- The first 64 bits are the network prefix.
- The next 64 bits are the interface identifier.
Link-Local Address
A link-local address is used to identify a device on a local network. It is not routable on the Internet. Link-local addresses are used for devices that do not need to connect to the Internet, such as printers and other network devices.An
example of a link-local address is fe80::200:ff:fe18:9876.The structure of a link-local address is as follows:
- The first 10 bits are the prefix.
- The next 54 bits are the interface identifier.
Multicast Address
A multicast address is used to send data to a group of devices on a network. Multicast addresses are used for applications such as video conferencing and online gaming.An example of a multicast address is ff02::1:ff00:1.The structure of a multicast address is as follows:
- The first 8 bits are the prefix.
- The next 4 bits are the flags.
- The next 112 bits are the group identifier.
Anycast Address, Match the description to the ipv6 addressing component
An anycast address is used to send data to the nearest device in a group of devices. Anycast addresses are used for applications such as load balancing and failover.An example of an anycast address is 2001:0db8:85a3:08d3:1319:8a2e:0370:7334.The structure of an anycast address is the same as a global unicast address.
Unspecified Address
The unspecified address is used to represent an unspecified device. It is the equivalent of the IPv4 address 0.0.0.0.An example of the unspecified address is ::.The structure of the unspecified address is as follows:
- All 128 bits are 0.
Questions and Answers: Match The Description To The Ipv6 Addressing Component
What is the purpose of a Global Unicast Address?
A Global Unicast Address uniquely identifies a single device on the internet, allowing for direct communication between two endpoints.
What is the structure of a Link-Local Address?
A Link-Local Address consists of a 64-bit prefix (fe80::/64) followed by a 64-bit interface identifier derived from the device’s MAC address.
How is a Multicast Address used?
A Multicast Address enables one-to-many communication, allowing a single source to transmit data to multiple receivers simultaneously.