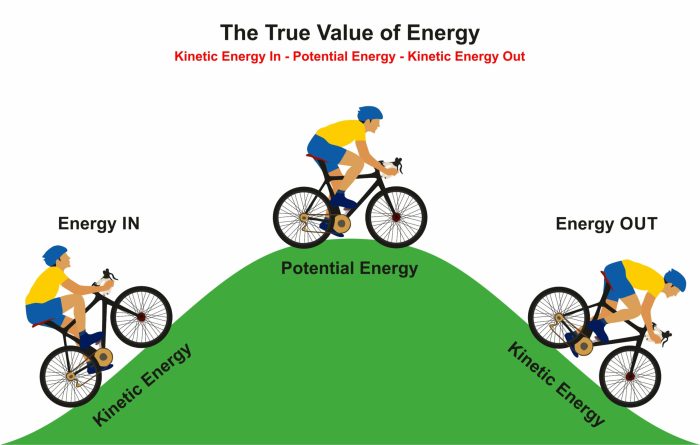
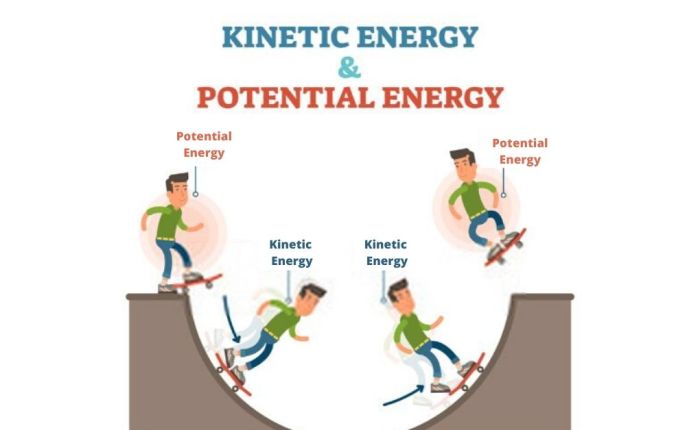
Embark on a journey into the realm of energy with our comprehensive Potential Energy vs Kinetic Energy Worksheet. This meticulously crafted guide unravels the intricacies of these fundamental energy forms, empowering you with a profound understanding of their nature, interconversion, and practical applications.
Delve into the concepts of potential and kinetic energy, exploring their distinct characteristics and manifestations in real-world scenarios. Discover the formulas that govern their calculation and witness the seamless transformation between these energy forms.
Potential and Kinetic Energy: Potential Energy Vs Kinetic Energy Worksheet
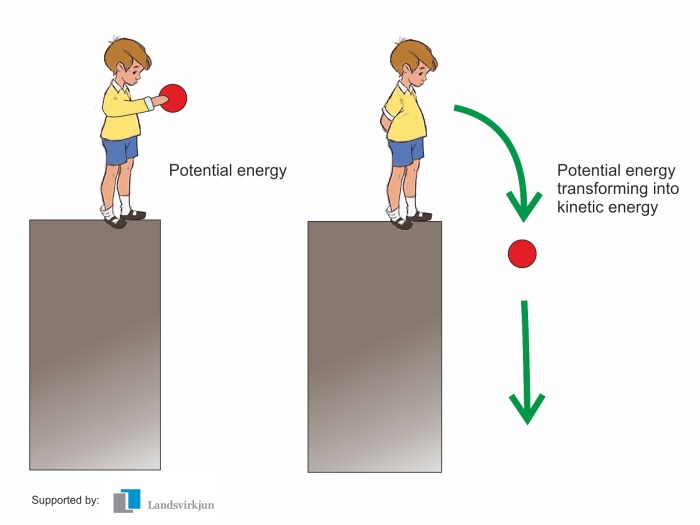
Energy exists in various forms, and potential and kinetic energy are two fundamental types. Understanding these forms is crucial in physics and numerous applications.
Understanding Potential and Kinetic Energy
Potential energy is the energy stored within an object due to its position or condition. It exists in two main forms: gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy. Gravitational potential energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its height above a reference point, while elastic potential energy is stored in a deformed object, such as a stretched spring.
Kinetic energy, on the other hand, is the energy of motion. It is directly proportional to the mass of the object and the square of its velocity. Kinetic energy is exhibited in moving objects, such as a rolling ball or a spinning top.
Comparing Potential and Kinetic Energy
| Characteristic | Potential Energy | Kinetic Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Stored Energy | Due to position or condition | Due to motion |
| Motion | No motion | Motion |
| Examples | Gravitational (e.g., a ball held above the ground), Elastic (e.g., a stretched rubber band) | Rolling ball, Spinning top |
Potential and kinetic energy are interconvertible. When an object falls, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. Conversely, when an object is lifted, its kinetic energy is transformed into potential energy.
Calculating Potential and Kinetic Energy
- Potential energy (gravitational): PE = mgh, where m is mass, g is acceleration due to gravity, and h is height
- Kinetic energy: KE = 1/2 mv², where m is mass and v is velocity
| Variable | Unit |
|---|---|
| Mass (m) | Kilograms (kg) |
| Acceleration due to gravity (g) | Meters per second squared (m/s²) |
| Height (h) | Meters (m) |
| Velocity (v) | Meters per second (m/s) |
Applications of Potential and Kinetic Energy
- Gravitational potential energy is used in hydroelectric power plants to generate electricity
- Elastic potential energy is utilized in springs, catapults, and bungee jumping
- Kinetic energy is employed in wind turbines, roller coasters, and vehicles
Conservation of Energy, Potential energy vs kinetic energy worksheet
The principle of conservation of energy states that the total amount of energy in an isolated system remains constant. Energy can be transformed from one form to another, but it cannot be created or destroyed. This principle applies to potential and kinetic energy, as they can be interconverted without any loss or gain of total energy.
FAQs
What is the key difference between potential and kinetic energy?
Potential energy is stored energy due to an object’s position or condition, while kinetic energy is energy of motion.
Can potential energy be converted into kinetic energy?
Yes, potential energy can be transformed into kinetic energy, as seen when a ball falls or a roller coaster descends.
What is the significance of energy conservation in potential and kinetic energy?
Energy conservation states that the total energy in a closed system remains constant, ensuring that energy is neither created nor destroyed, only transformed.