Embark on an exciting journey with the “Ionic & Covalent Compound Naming Race,” a game that transforms the intricacies of chemical nomenclature into a thrilling competition. Delve into the world of ionic and covalent bonds, unraveling their distinct characteristics and the rules that govern their naming conventions.
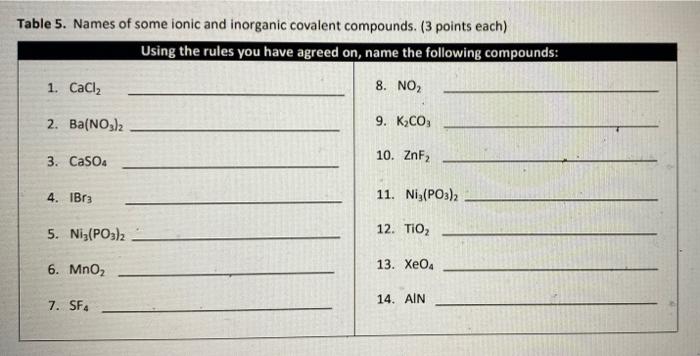
Through this interactive experience, you’ll not only sharpen your understanding of compound naming but also gain insights into the fundamental principles that underpin chemical bonding.
Ionic and Covalent Compound Naming: Ionic & Covalent Compound Naming Race
Ionic and covalent compounds are two main types of chemical compounds that differ in the nature of their chemical bonds. Ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions.
Covalent compounds, on the other hand, are formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms. The naming conventions for these two types of compounds are distinct and reflect their different bonding characteristics. Ionic Compound Naming:Ionic compounds are named using the names of the constituent ions.
The positive ion (cation) is named first, followed by the negative ion (anion). The name of the cation is typically the same as the element name, while the name of the anion is derived from the element name with the suffix “-ide”.
For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) is an ionic compound formed between the sodium cation (Na+) and the chloride anion (Cl-). Covalent Compound Naming:Covalent compounds are named using the prefixes that indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the molecule.
The prefixes used are: mono- (1), di- (2), tri- (3), tetra- (4), penta- (5), hexa- (6), hepta- (7), octa- (8), nona- (9), and deca- (10). The name of the first element is followed by the name of the second element with the suffix “-ide”.
For example, carbon dioxide (CO2) is a covalent compound formed between one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
Nomenclature Race

The ionic & covalent compound naming race is a hypothetical game designed to enhance understanding of compound naming. The game involves two or more players who compete to name the correct chemical compounds based on the given formulas or names.
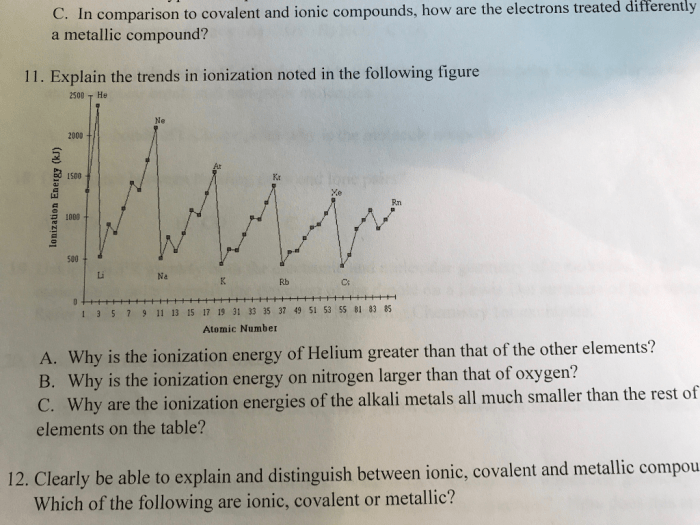
Rules of the Game:
- Players are given a list of chemical formulas or names.
- The first player to correctly name the compound wins a point.
- The player with the most points at the end of the game wins.
Objectives of the Game:
- To improve understanding of ionic and covalent compound naming conventions.
- To develop quick thinking and problem-solving skills.
- To make learning about chemical compounds more engaging and interactive.
Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding
| Property | Ionic Bonding | Covalent Bonding |
|---|---|---|
| Bond Formation | Transfer of electrons | Sharing of electrons |
| Properties of Resulting Compounds | – High melting and boiling points
|
– Lower melting and boiling points
|
| Examples | – Sodium chloride (NaCl)
|
– Methane (CH4)
|
Applications of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
Ionic and covalent compounds have numerous applications in everyday life. Ionic Compounds:
Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Table salt, used as a seasoning and preservative
Potassium chloride (KCl)
Fertilizer, used to replenish potassium in soil
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
Antacid, used to neutralize stomach acid Covalent Compounds:
Methane (CH4)
Natural gas, used as a fuel source
Water (H2O)
Essential for life, used for drinking, cleaning, and industrial purposes
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Used in fire extinguishers and as a refrigerant
Essential Questionnaire
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons, resulting in the formation of charged ions, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
How can I participate in the “Ionic & Covalent Compound Naming Race”?
This game is hypothetical and not available for participation.
What are the applications of ionic and covalent compounds?
Ionic compounds are commonly found in salts, while covalent compounds are found in a wide range of substances, including water, organic molecules, and plastics.