Nihss stroke scale answers group d – Delving into the intricacies of the NIHSS Stroke Scale Group D, this comprehensive guide unveils its profound significance in stroke assessment and management. Understanding Group D’s components and scoring system empowers clinicians with valuable insights into stroke severity, prognosis, and treatment strategies.
This in-depth exploration delves into the clinical applications of Group D scores, guiding treatment decisions and patient monitoring. By recognizing the limitations and considerations associated with Group D, clinicians can harness its full potential while ensuring accuracy and reliability in clinical practice.
Understanding the NIHSS Stroke Scale Group D: Nihss Stroke Scale Answers Group D

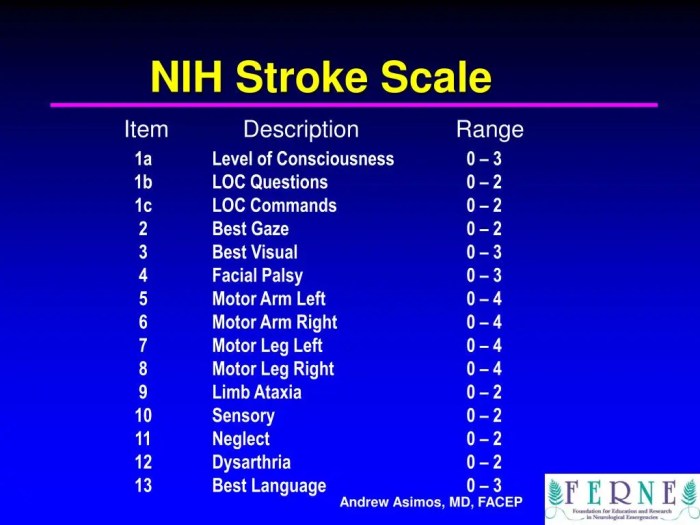
Group D of the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) assesses consciousness, language, and neglect. It plays a crucial role in determining stroke severity and guiding treatment decisions.
Group D consists of three components: level of consciousness, language comprehension, and neglect.
- Level of consciousnessis assessed on a scale of 0 to 3, with 0 indicating alertness and 3 indicating coma.
- Language comprehensionis assessed on a scale of 0 to 2, with 0 indicating normal comprehension and 2 indicating severe aphasia.
- Neglectis assessed on a scale of 0 to 2, with 0 indicating no neglect and 2 indicating severe neglect.
Scoring and Interpretation of Group D, Nihss stroke scale answers group d
The total score for Group D ranges from 0 to 7. A score of 0 indicates no deficits, while a score of 7 indicates severe deficits in consciousness, language, and neglect.
Scores for each component are interpreted as follows:
- Level of consciousness:0 = alert, 1 = drowsy, 2 = stuporous, 3 = comatose
- Language comprehension:0 = normal, 1 = mild aphasia, 2 = severe aphasia
- Neglect:0 = no neglect, 1 = mild neglect, 2 = severe neglect
Impact of Group D on Stroke Outcomes
Group D scores have been shown to correlate with stroke severity, functional outcomes, and mortality.
- Higher Group D scores are associated with more severe strokes.
- Patients with higher Group D scores have worse functional outcomes at discharge and follow-up.
- Higher Group D scores are associated with increased mortality.
Clinical Applications of Group D
Group D scores are used in clinical practice to:
- Determine stroke severity
- Guide treatment decisions
- Monitor patient progress
- Predict functional outcomes and mortality
Limitations and Considerations
Limitations of using Group D include:
- Subjectivity in scoring
- Influence of pre-existing cognitive deficits
- Limited sensitivity in mild strokes
To address these limitations, it is important to use Group D in conjunction with other clinical information and to consider the patient’s pre-stroke cognitive status.
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of Group D in the NIHSS Stroke Scale?
Group D assesses consciousness, gaze, and visual fields, providing crucial insights into the severity and location of neurological deficits in stroke patients.
How are Group D scores interpreted?
Higher scores indicate more severe neurological impairments, with each component contributing specific points to the overall score.
What is the prognostic value of Group D scores?
Research has established a strong correlation between Group D scores and stroke severity, functional outcomes, and mortality, making them valuable predictors of patient prognosis.