Bolt action rifle parts diagram, a comprehensive guide to the intricate workings of these precision firearms. Delve into the history, components, assembly, troubleshooting, and customization of bolt action rifles, empowering you with a deeper understanding and appreciation for these iconic weapons.
Unveiling the inner workings of bolt action rifles, this guide provides a detailed exploration of each component, its function, design, materials, and manufacturing process. With step-by-step instructions and safety precautions, you’ll gain the confidence to assemble and disassemble your rifle with ease.
Bolt Action Rifle Parts Diagram Overview
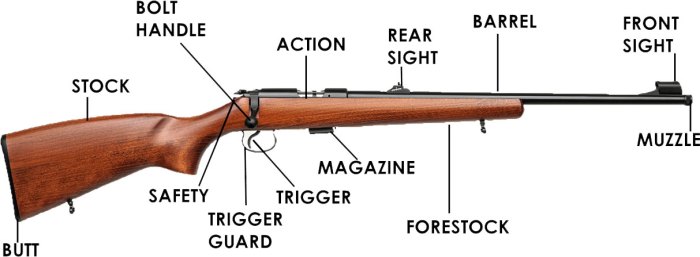
A bolt action rifle parts diagram is an essential tool for understanding the intricate workings of a bolt action rifle. It provides a visual representation of all the components that make up the rifle, allowing for easy identification and understanding of their functions.
Bolt action rifles have a long and storied history, dating back to the late 19th century. They are known for their accuracy, reliability, and power, making them a popular choice for hunters, target shooters, and military personnel alike.
Types of Bolt Action Rifles
There are several different types of bolt action rifles, each with its own unique features and applications. Some of the most common types include:
- Single-shot rifles:These rifles are designed to fire one round at a time and must be manually reloaded after each shot.
- Magazine-fed rifles:These rifles use a magazine to hold multiple rounds of ammunition, allowing for faster reloading.
- Semi-automatic rifles:These rifles can fire multiple rounds of ammunition in rapid succession without the need for manual reloading.
Key Components of a Bolt Action Rifle
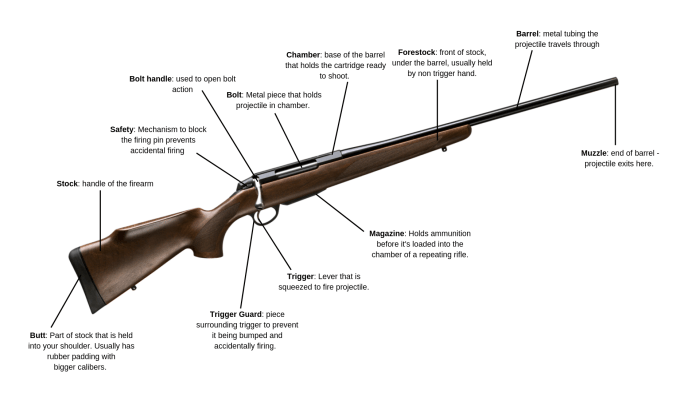
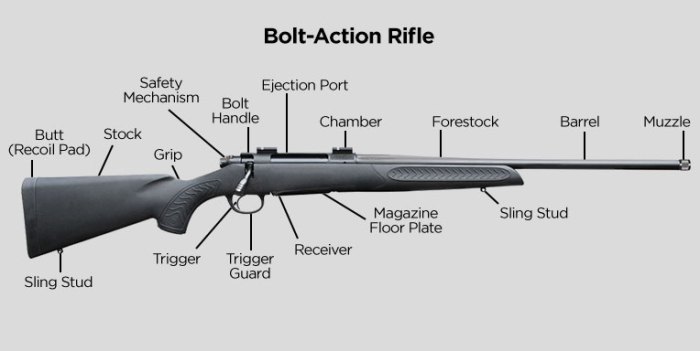
Bolt action rifles, renowned for their precision and reliability, comprise several essential components that work in harmony to deliver exceptional performance. Understanding these components is crucial for proper maintenance, repair, and operation of these firearms.
Receiver
The receiver serves as the foundation of the rifle, housing the bolt, barrel, and trigger assembly. It is typically crafted from durable materials like steel or aluminum to withstand the rigors of firing. The receiver provides a secure mounting point for the barrel and ensures proper alignment of the bolt and trigger.
Bolt
The bolt is the heart of the bolt action rifle, responsible for loading, firing, and extracting cartridges. It consists of a bolt body, extractor, and firing pin. The bolt body houses the firing pin and moves back and forth within the receiver to complete the firing cycle.
The extractor grips the spent cartridge case and ejects it after firing, while the firing pin strikes the primer to ignite the cartridge.
Barrel
The barrel is the channel through which the bullet travels. It is precisely rifled with spiral grooves that impart spin to the bullet, stabilizing its trajectory. The barrel’s length, diameter, and rifling characteristics significantly influence the rifle’s accuracy and range.
Trigger, Bolt action rifle parts diagram
The trigger is the mechanism that initiates the firing process. When pulled, it releases the sear, allowing the firing pin to strike the primer and ignite the cartridge. Triggers can vary in design and sensitivity, affecting the accuracy and consistency of the rifle.
Stock
The stock provides a stable platform for the rifle and allows the shooter to control it effectively. It typically consists of a buttstock, forearm, and grip. The buttstock absorbs recoil and provides a comfortable shooting position, while the forearm and grip facilitate proper handling and aiming.
Detailed Analysis of Bolt Action Rifle Parts
Bolt action rifles are renowned for their precision and reliability, and this is largely due to the intricate design and construction of their individual parts. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of the rifle, and understanding their design, materials, and manufacturing processes is essential for appreciating the craftsmanship behind these iconic firearms.
Bolt
The bolt is the heart of a bolt action rifle, responsible for chambering and extracting cartridges, as well as locking the action securely during firing. Typically made from high-strength steel, the bolt consists of several key components:
- Bolt Body:The main housing of the bolt, which contains the firing pin and extractor.
- Bolt Handle:The lever used to manually operate the bolt, providing leverage for smooth cycling.
- Firing Pin:The component that strikes the primer of the cartridge, initiating the firing process.
- Extractor:The mechanism that grips the spent cartridge case and pulls it out of the chamber.
The bolt is often precision-machined from a single piece of steel, ensuring strength and reliability. Its design and construction must allow for smooth and consistent operation, as any imperfections can affect the accuracy and reliability of the rifle.
Assembly and Disassembly of a Bolt Action Rifle: Bolt Action Rifle Parts Diagram
Assembling and disassembling a bolt action rifle requires meticulous attention to detail and adherence to safety protocols. This guide will provide a step-by-step breakdown of the process, ensuring proper handling and maintenance of your firearm.
Safety Precautions
- Always ensure the firearm is unloaded before attempting any assembly or disassembly.
- Wear appropriate safety gear, including eye protection and gloves.
- Work in a well-lit, stable environment.
- Follow all manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
Disassembly
- Remove the Bolt:Open the bolt by lifting the bolt handle and pulling the bolt straight back. Remove the bolt from the receiver.
- Separate the Barrel from the Receiver:For most bolt action rifles, a locking lever or release mechanism needs to be manipulated to detach the barrel from the receiver. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific details.
- Disassemble the Bolt:The bolt can be further disassembled into its individual components, including the firing pin, extractor, and ejector. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific disassembly procedures.
Assembly
- Assemble the Bolt:Reassemble the bolt components in reverse order of disassembly.
- Attach the Barrel to the Receiver:Align the barrel with the receiver and engage the locking mechanism or release lever to secure the barrel in place.
- Insert the Bolt:Insert the bolt into the receiver and push it forward until it locks into place.
Remember, assembling and disassembling a bolt action rifle is a delicate process that requires careful attention to detail and safety. Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific procedures and consult a qualified gunsmith if necessary.
Troubleshooting Common Bolt Action Rifle Issues
Bolt action rifles are known for their accuracy and reliability, but even these firearms can experience occasional issues. Here’s a guide to identifying and troubleshooting common problems that may arise with bolt action rifles:
Failure to Extract
- Dirty or corroded chamber:Clean the chamber thoroughly to remove any debris or corrosion that may be preventing the cartridge case from extracting.
- Weak extractor:Replace the extractor if it is worn or damaged and no longer able to securely grip the cartridge case.
- Bent or damaged bolt:Inspect the bolt for any bends or damage that may be interfering with the extraction process.
Failure to Eject
- Dirty or obstructed ejector:Clean the ejector and its surrounding area to remove any debris or obstructions that may be preventing the cartridge case from ejecting.
- Weak ejector spring:Replace the ejector spring if it is weak or broken, as it is responsible for providing the force to eject the cartridge case.
- Misaligned ejector:Ensure that the ejector is properly aligned with the cartridge case to allow for smooth ejection.
Difficulty Cycling the Bolt
- Dirty or dry action:Clean and lubricate the bolt and its components to reduce friction and ensure smooth operation.
- Obstructed firing pin:Inspect the firing pin for any debris or obstructions that may be preventing it from moving freely.
- Damaged bolt handle:Replace the bolt handle if it is bent or damaged, as it may be hindering the cycling process.
Misfires
- Faulty firing pin:Replace the firing pin if it is broken or damaged and no longer able to strike the primer with sufficient force.
- Weak firing pin spring:Replace the firing pin spring if it is weak or broken, as it provides the energy to drive the firing pin forward.
- Improper headspacing:Ensure that the cartridge is properly headspaced in the chamber to allow for proper ignition.
Customization and Modifications of Bolt Action Rifles
Bolt action rifles offer a wide range of customization and modification options to enhance their performance, aesthetics, and ergonomics. From simple upgrades to comprehensive overhauls, the possibilities are virtually limitless.
Understanding bolt action rifle parts diagrams can be crucial for maintenance and safety. However, for a broader perspective on firearms laws, consider checking out unit 1 lesson 5 joshua’s law . It offers insights into legal responsibilities and safe handling practices.
Returning to the topic of bolt action rifles, mastering their parts diagrams empowers you with the knowledge to confidently assemble, disassemble, and maintain your firearm.
Barrel and Action Upgrades
- Barrel replacement:Swapping out the original barrel with a higher-quality or specialized barrel can significantly improve accuracy and range.
- Trigger upgrades:Replacing the stock trigger with a lighter or adjustable trigger enhances precision and reduces shooter fatigue.
- Action tuning:Smoothing and lightening the action can improve cycling speed and reduce recoil.
Stock Modifications
- Stock replacement:Installing an aftermarket stock with improved ergonomics and materials can enhance comfort and handling.
- Adjustable stock:Stocks with adjustable length of pull and cheek risers allow for a customized fit to the shooter’s physique.
- Custom bedding:Bedding the action into the stock ensures a precise fit, reducing vibration and improving accuracy.
Optics and Accessories
- Scope mounting:Installing a high-quality scope and mount provides precise aiming and increased range.
- Bipod installation:A bipod stabilizes the rifle for improved accuracy when shooting from a prone position.
- Suppressor attachment:A suppressor reduces recoil and muzzle noise, making the rifle more comfortable to shoot.
Importance of Proper Gunsmithing
It is crucial to entrust customization and modifications to a qualified gunsmith. Improper installation or alterations can compromise safety, accuracy, and reliability. Professional gunsmiths have the necessary skills, tools, and experience to ensure proper execution of these modifications.
Safety Considerations for Bolt Action Rifles

Bolt action rifles are powerful and potentially dangerous weapons, so it’s crucial to prioritize firearm safety when using them. Proper handling, storage, and maintenance are essential to prevent accidents and ensure the well-being of yourself and others. Additionally, firearm owners have legal responsibilities to ensure their weapons are used responsibly and safely.
Safe Handling
* Always treat the rifle as if it’s loaded, even if you know it’s not.
- Keep the rifle pointed in a safe direction at all times, even when unloading or cleaning it.
- Never point the rifle at anything you don’t intend to shoot.
- Be aware of your surroundings and potential hazards before firing.
- Only load the rifle when you’re ready to shoot.
Safe Storage
* Store the rifle unloaded and locked in a secure location, inaccessible to unauthorized individuals.
- Use a trigger lock or other locking device to prevent accidental discharge.
- Store ammunition separately from the rifle.
- Keep the rifle and ammunition in a cool, dry place, away from moisture and heat.
Safe Maintenance
* Regularly inspect the rifle for any signs of damage or malfunction.
- Clean and lubricate the rifle according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Never attempt to repair or modify the rifle yourself unless you’re a qualified gunsmith.
Legal Responsibilities
* Know and obey all local, state, and federal laws regarding firearm ownership and use.
- Report lost or stolen firearms to the authorities immediately.
- Use firearms only for lawful purposes.
- Never use a firearm under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key components of a bolt action rifle?
The receiver, bolt, barrel, trigger, and stock are the essential components of a bolt action rifle.
How do I safely disassemble a bolt action rifle?
Refer to the step-by-step guide in this document, ensuring you follow all safety precautions.
What are some common troubleshooting issues with bolt action rifles?
Failure to extract, failure to feed, and misfires are common issues that can be addressed with proper troubleshooting.