Surgical kit for feline spay is an indispensable component of a successful spaying procedure. It contains a specialized set of instruments designed to ensure precision, safety, and efficiency during the surgery. This guide provides an in-depth overview of the essential instruments included in a surgical kit for feline spay, their functions, and usage.
Additionally, it offers a step-by-step guide to the feline spay procedure, preoperative preparation, postoperative care, potential complications, and alternative spaying methods.
Feline spaying is a routine surgical procedure that involves the removal of a female cat’s reproductive organs, typically the ovaries and uterus. It is commonly performed to prevent unwanted pregnancies, reduce the risk of certain reproductive diseases, and improve the overall health and well-being of the cat.
Surgical Instruments
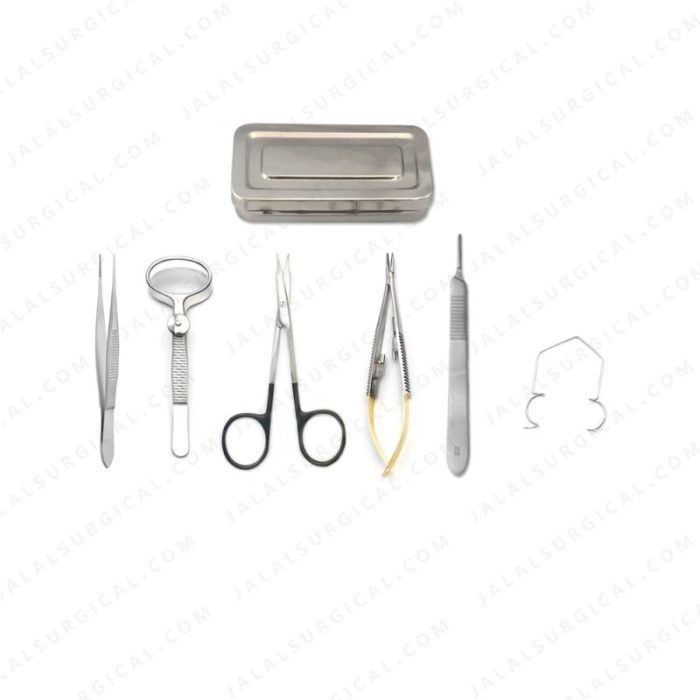
Surgical instruments are the backbone of any surgical procedure, providing the surgeon with the tools necessary to perform precise and efficient operations. In the context of feline spay, a specialized kit of instruments is essential to ensure the safety and well-being of the patient.
Each instrument within the kit serves a specific function, ranging from tissue manipulation to suture placement. Understanding the purpose and proper usage of these instruments is crucial for successful surgical outcomes.
Essential Instruments for Feline Spay
| Instrument Name | Description | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scalpel | A sharp, single-edged blade used for making incisions. | Incision of skin and subcutaneous tissues. | [Image of a scalpel] |
| Hemostat | A clamp-like instrument used to control bleeding. | Clamping blood vessels to prevent excessive bleeding. | [Image of a hemostat] |
| Tissue Forceps | A delicate, toothed instrument used to grasp and manipulate tissues. | Handling and holding tissues during dissection and suturing. | [Image of tissue forceps] |
| Suture Needle | A fine, curved needle used for suturing tissues together. | Closure of incisions and ligation of blood vessels. | [Image of a suture needle] |
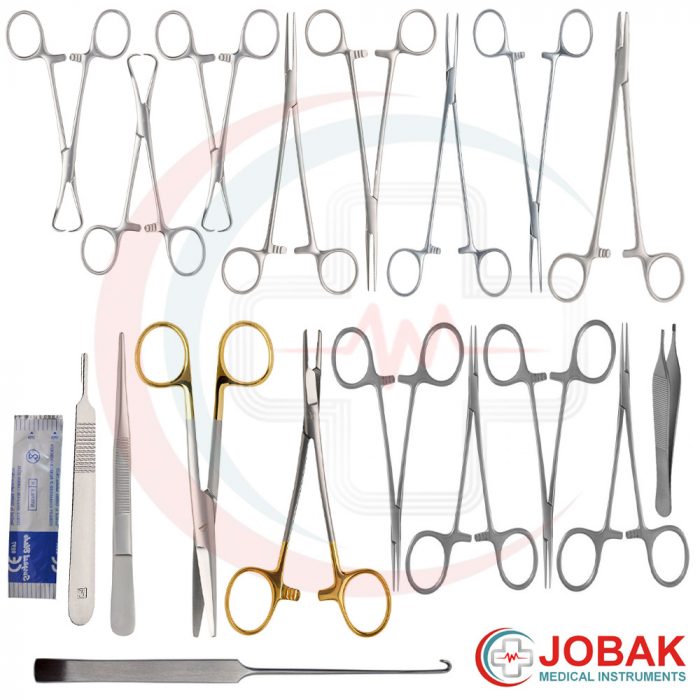
Spay Procedure Overview
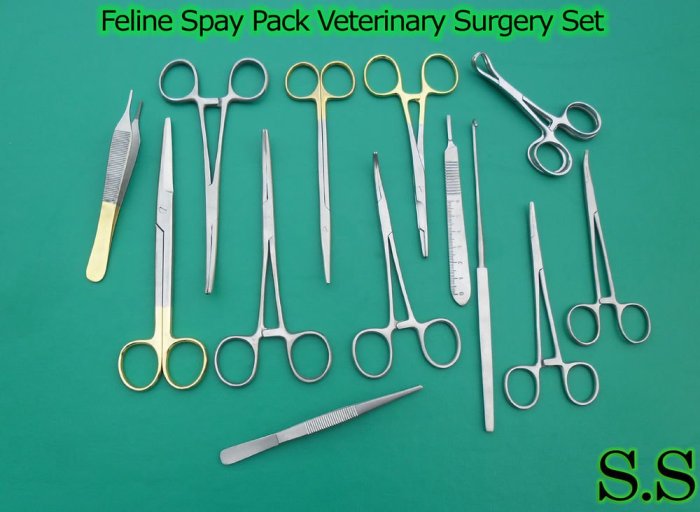
Feline spaying is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the female reproductive organs, typically the ovaries and uterus. This procedure is commonly performed to prevent unwanted litters, reduce the risk of certain reproductive cancers, and eliminate the hormonal influence of the reproductive cycle.
The spay procedure typically involves several steps, including:
Surgical Access Techniques
There are two main surgical approaches used to access the reproductive organs during a feline spay:
- Ventral midline incision:This technique involves making an incision along the midline of the abdomen, providing direct access to the reproductive organs.
- Flank incision:This technique involves making an incision on the side of the abdomen, allowing access to the reproductive organs through a smaller incision.
The choice of surgical approach depends on factors such as the surgeon’s preference, the patient’s anatomy, and any potential complications.
If you’re a vet, you’ll need a surgical kit for feline spay. A surgical kit typically includes a scalpel, forceps, and sutures. Speaking of stacks, did you know that hiro has a stack of cards ? Back to the topic, a surgical kit is essential for any vet who performs feline spays.
Step-by-Step Overview, Surgical kit for feline spay
The following table provides a step-by-step overview of the feline spay procedure, along with potential complications associated with each step:
| Step | Procedure | Potential Complications |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Surgical access | Hemorrhage, infection, incisional herniation |
| 2 | Identification and ligation of uterine horns | Uterine hemorrhage, retained ovary syndrome |
| 3 | Removal of ovaries | Ovarian hemorrhage, ovarian remnant syndrome |
| 4 | Closure of surgical site | Infection, dehiscence |
Preoperative Preparation

Ensuring a successful feline spay requires meticulous preoperative preparation. This involves several crucial steps that enhance patient safety and surgical outcomes.
The importance of preoperative measures cannot be overstated. They help minimize surgical risks, ensure a smooth anesthetic recovery, and promote optimal healing.
Fasting
- Fasting before surgery is essential to prevent aspiration of stomach contents into the lungs during anesthesia.
- Solid food should be withheld for 12 hours, while water can be offered up to 2 hours before surgery.
Anesthesia
- Anesthesia is crucial for pain management and patient safety during surgery.
- Veterinarians will administer a combination of anesthetic drugs to induce unconsciousness and prevent pain.
- Preoperative bloodwork may be recommended to assess the patient’s overall health and suitability for anesthesia.
Surgical Site Preparation
- The surgical site must be thoroughly prepared to minimize the risk of infection.
- The area around the incision is shaved and disinfected with an antiseptic solution.
- Drapes are placed to isolate the surgical area from the rest of the body.
Postoperative Care

After the spaying procedure, your feline companion will require proper postoperative care to ensure a smooth and comfortable recovery. Here’s an overview of what to expect and how to care for your cat during this period.
Postoperative care can be divided into immediate care and long-term care. Immediate care refers to the first 24-48 hours after surgery, while long-term care extends beyond this initial period.
Immediate Postoperative Care
- Monitor your cat closely for any signs of discomfort or complications.
- Provide a quiet and comfortable space for your cat to rest.
- Restrict your cat’s activity to prevent excessive movement and strain on the incision site.
- Administer pain medication as prescribed by your veterinarian.
- Keep the incision site clean and dry.
- Observe your cat’s eating and drinking habits and ensure adequate hydration.
Long-Term Postoperative Care
- Continue to restrict your cat’s activity for 10-14 days to allow the incision to heal properly.
- Monitor the incision site for any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge.
- Avoid bathing your cat for at least 10 days after surgery.
- Gradually increase your cat’s activity level as tolerated.
- Attend scheduled follow-up appointments with your veterinarian for incision checks and suture removal.
Potential Complications
Spaying a feline is a relatively safe procedure, but like any surgery, there are potential complications that can occur. It is important to be aware of these complications so that you can make informed decisions about your cat’s care.
The most common complications associated with feline spay include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Anesthesia complications
- Urinary tract complications
- Gastrointestinal complications
In most cases, these complications can be treated successfully. However, it is important to seek veterinary care immediately if you notice any of the following symptoms:
- Excessive bleeding
- Discharge from the incision
- Swelling or redness around the incision
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
By being aware of the potential complications associated with feline spay, you can help ensure that your cat has a safe and healthy recovery.
| Complication | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bleeding | Damage to blood vessels during surgery | Excessive bleeding from the incision | Surgery to stop the bleeding |
| Infection | Bacteria entering the incision | Discharge from the incision, swelling, redness | Antibiotics |
| Anesthesia complications | Allergic reaction to anesthesia, respiratory problems | Difficulty breathing, swelling of the face | Emergency treatment |
| Urinary tract complications | Damage to the urinary tract during surgery | Difficulty urinating, blood in the urine | Surgery to repair the damage |
| Gastrointestinal complications | Damage to the gastrointestinal tract during surgery | Vomiting, diarrhea | Surgery to repair the damage |
Alternative Spaying Methods: Surgical Kit For Feline Spay
Traditional surgical spaying, while effective, is not the only option available. Alternative methods like laparoscopic or laser-assisted spaying offer advantages in certain situations. Let’s explore these methods and their differences from traditional spaying.
Laparoscopic Spaying
- Involves making small incisions and inserting a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube) to visualize and manipulate the ovaries and uterus.
- Less invasive, leading to reduced pain and faster recovery time.
- Requires specialized equipment and training for the surgeon.
- May be more expensive than traditional spaying.
Laser-Assisted Spaying
- Utilizes a laser to seal the blood vessels and cut tissues, resulting in minimal bleeding.
- Offers precise and bloodless surgery, reducing the risk of complications.
- Can be more expensive than traditional spaying.
- Requires specialized equipment and training for the surgeon.
Clarifying Questions
What are the essential instruments included in a surgical kit for feline spay?
A surgical kit for feline spay typically includes instruments such as a scalpel, scissors, forceps, hemostats, and suture needles.
What are the potential complications associated with feline spay?
Potential complications include bleeding, infection, and anesthetic complications. These complications are relatively rare but can occur in any surgical procedure.
What are the advantages of laparoscopic spaying?
Laparoscopic spaying offers advantages such as reduced pain, faster recovery time, and less scarring compared to traditional surgical spaying.